在本章中,你将学到如何从零使用Sbt来搭建一个Scala工程,如何将Scala工程导入Intellij IDEA集成开发环境。同时,我们将使用scalatest以TDD的方式来编写代码。
本章的要点包括:
- 下载并使用sbt: http://www.scala-sbt.org/
- 使用Intellij IDEA编写Scala:https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/
- 使用scalatest进行测试驱动的开发:http://www.scalatest.org/
安装Sbt
在官网 http://www.scala-sbt.org/download.html 提供了 sbt 的下载,因为网络原因,很有可能下载失败。这里您可以使用华龙海数公司提供的链接下载:https://file.hualongdata.com/sbt-0.13.16.tgz 。
下载后解压并设置系统环境变量,SBT 就安装好了。
Linux/Unix/Mac
1 | tar zxf sbt-0.13.16.tgz -C ~/ |
添加如下内容到 ~/.bash_profile:
1 | export SBT_HOME="$HOME/sbt" |
注:若不想重启系统的话,请在终端执行命令使配置生效:. ~/.bash_profile。
Windows
Windows 安装见官方文档:http://www.scala-sbt.org/1.x/docs/zh-cn/Installing-sbt-on-Windows.html。对应的,你也可以通过华龙海数公司提供的链接下载:*https://file.hualongdata.com/sbt-0.13.16.tgz*。
建立Scala SBT工程
建立工程配置文件
1 | mkdir scala-starter |
对于一个Scala工程项目,配置文件非常的简单。你只需要设置 build.sbt 和 project/build.properties 两个文件即可。在build.sbt文件配置项目选项,如:名称、Scala版本、库依赖……。在project/build.properties文件指定用于构建使用的Sbt具体版本。
在build.sbt文件内,我们只指定了3个配置选项:
- name 项目的名字
- scalaVersion 编译此项目使用的Scala版本
- libraryDependencies 依赖的第3方库
让我们在终端输入 sbt 命令(你需要按上一节的方式安装好SBT),当看到如下界面就代表Scala工程项目建立成功。
1 | $ sbt |
注:你所看到的信息可能略有不同,因为可能安装了不同的插件及在不同的目录。
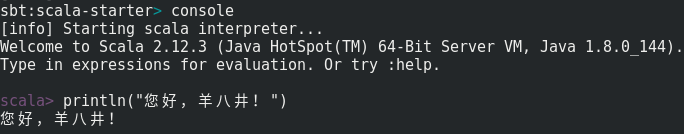
让我们在sbt控制台中输入 console 命令,先来试试Scala语言。
使用IDEA开发
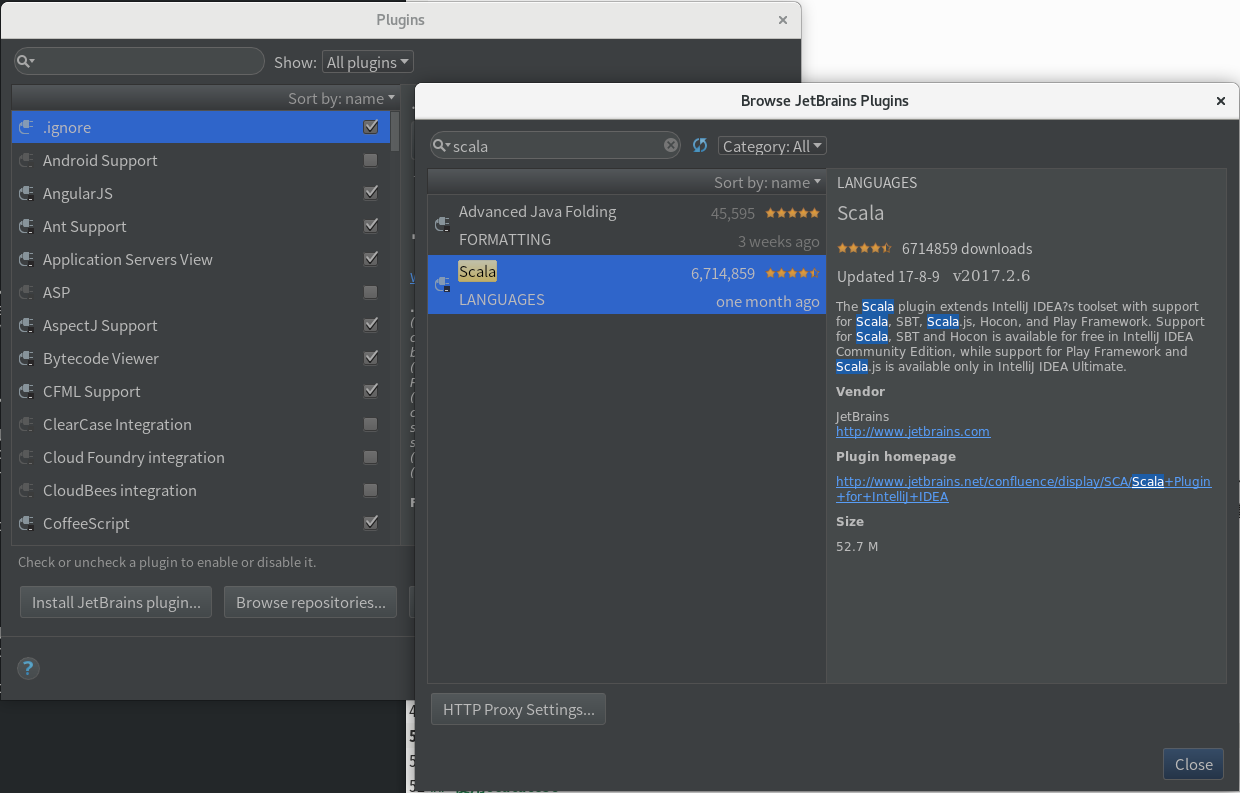
首先需要安装 IDEA 的Scala插件。
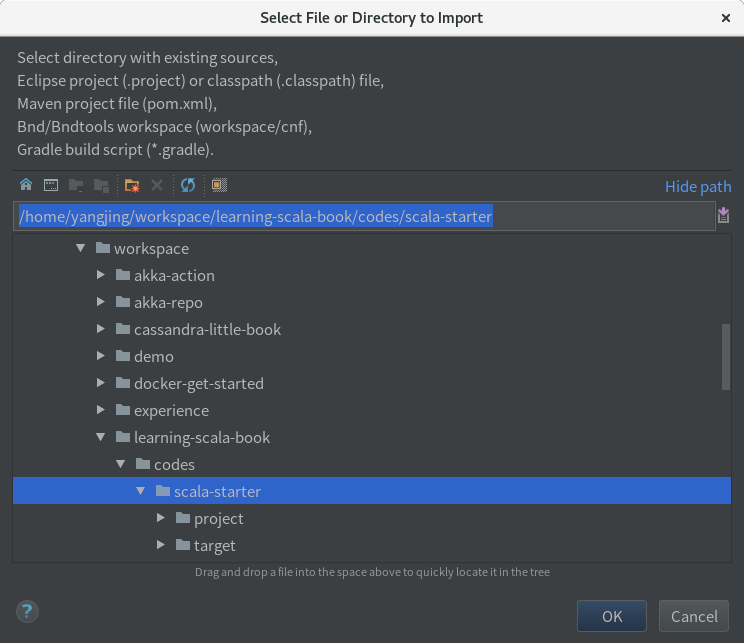
选择刚才建立好的 scala-starter 项目根目录:
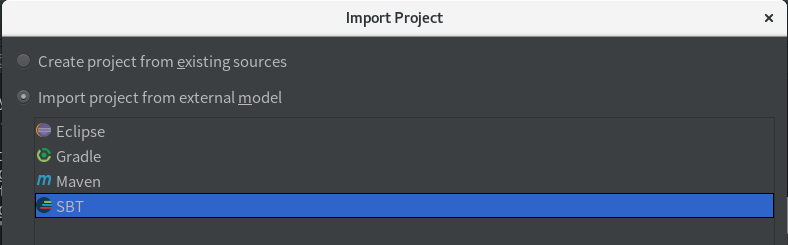
使用 SBT 方式导入项目:
选中 *Use SBT shell for build and import(requires sbt 0.13.5+)*,并点击 finish 完成:
待IDEA下载完依赖后就会打开 scala-starter 项目,显示如下:
这里,我们还没有任务Scala代码。按惯例,我们先来实现一个Scala版的 **hello, world!**。首先,我们需要建立Scala代码目录结构,可以在IDEA中创建目录,也可以通过命令行创建。这里,我们使用命令行来创建:
1 | mkdir -p src/main/scala |
我们在IDEA中新建一个 Helloword 类。首先选中 src/main/scala 文件夹,点击鼠标右键,并选择新建 Scala class ,在 Name 输入框输入 scalastarter.Helloword ,在 Kind 输入框选择 Object 。如:
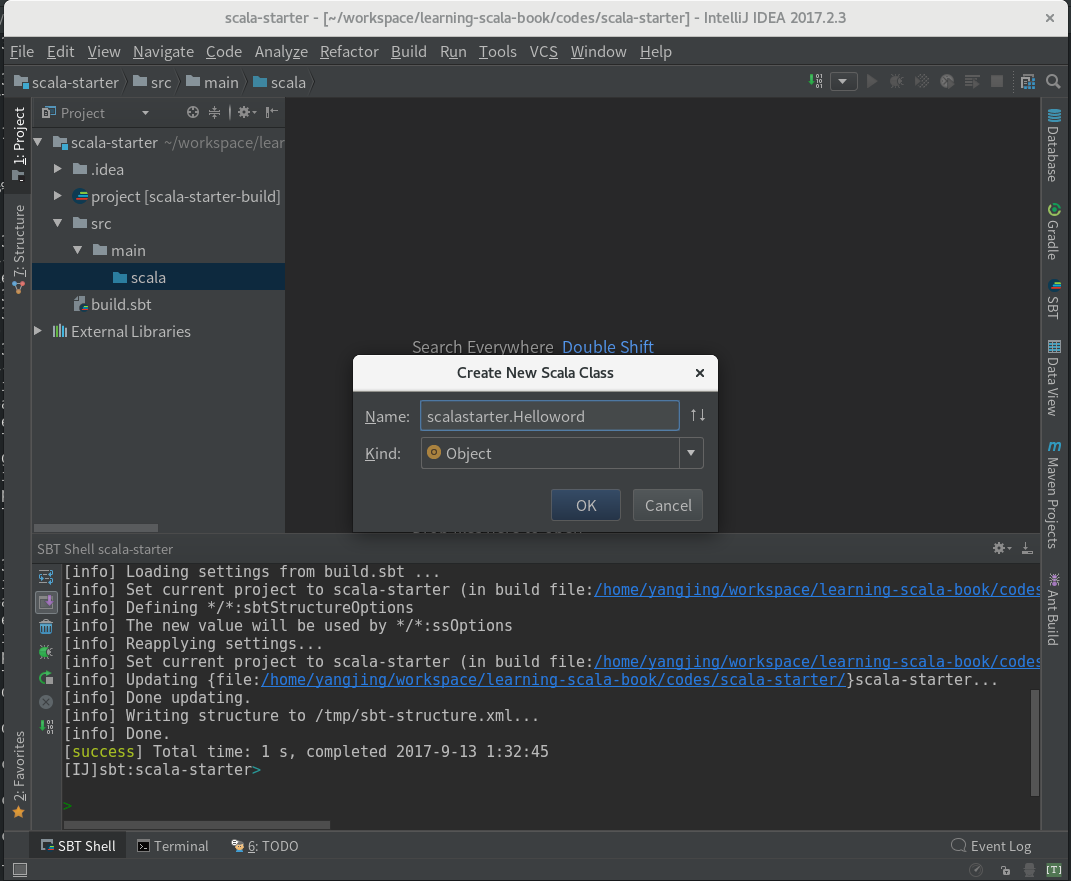
修改 Helloword 代码如下:
1 | object Helloword extends App { |
点击 object Helloword extends App { 右侧的绿色箭头小图标来运行 Helloword 程序,将在 Run 窗口中显示运行结果:
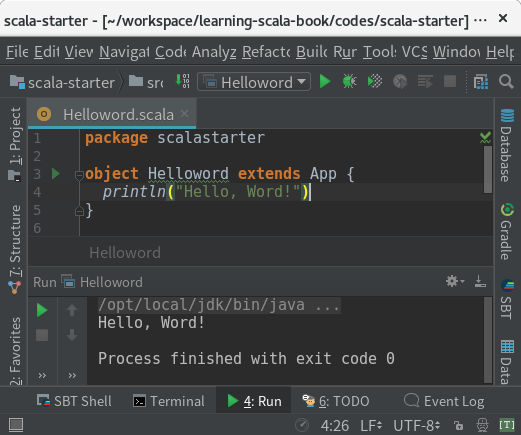
至此,我们从命令行创建 Scala工程项目,导入到 IDEA,创建并运行 Helloword。我们走通了一个工程化的使用Scala编写 helloword 的全流程,感觉良好。
使用Scalatest
在开发实践中,TDD(测试驱动开发)是一个很好的开始方式。当然,Scala对TDD有着良好的支持,依托IDEA的强大功能,我们可以方便、优雅的实践TDD。在Scala开发中,推荐使用 scalatest 来实践测试驱动开发。
首先,我们需要创建 src/test/scala 目录来放测试代码,这次我们直接在IDEA中创建目录。在IDEA左侧的 Project 视图的 src 文件夹上点鼠标右键新建目录 test/scala,现在工程的目录结构如下:
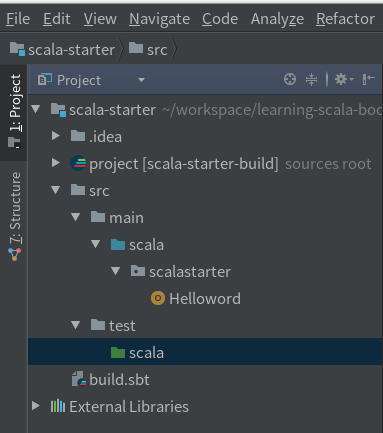
我们通过一个Scala类来演示scalatest的使用,这是一个很简单,但足以激发你的兴趣的类:
1 | class Friendships { |
Friendships 是一个很简单的类,它保存了一个私有的Map[String, List[String]] 变量:friendships ,朋友关系。同时提供了3个函数来对朋友关系进行操作,它们分别是:获取某人的朋友列表、判断一个人是否是某人的朋友、添加一个人到某人的朋友列表中。现在3个函数都还没有真实的功能实现,不用急,先让我们把测试跑起来。通过 红灯 - 绿灯 - 重构 的形式来实现这些功能。
从IDEA打开的 Friendships.scala 代码上,把光标放到 Friendships 类里面,同时按 Ctrl + Shirt + T 键,IDEA会自动生成以 Test 结尾的单元测试类:FriendshipsTest.scala。这里选择超类为:org.scalatest.WordSpec,并勾上下边窗口列出的3个成员方式。
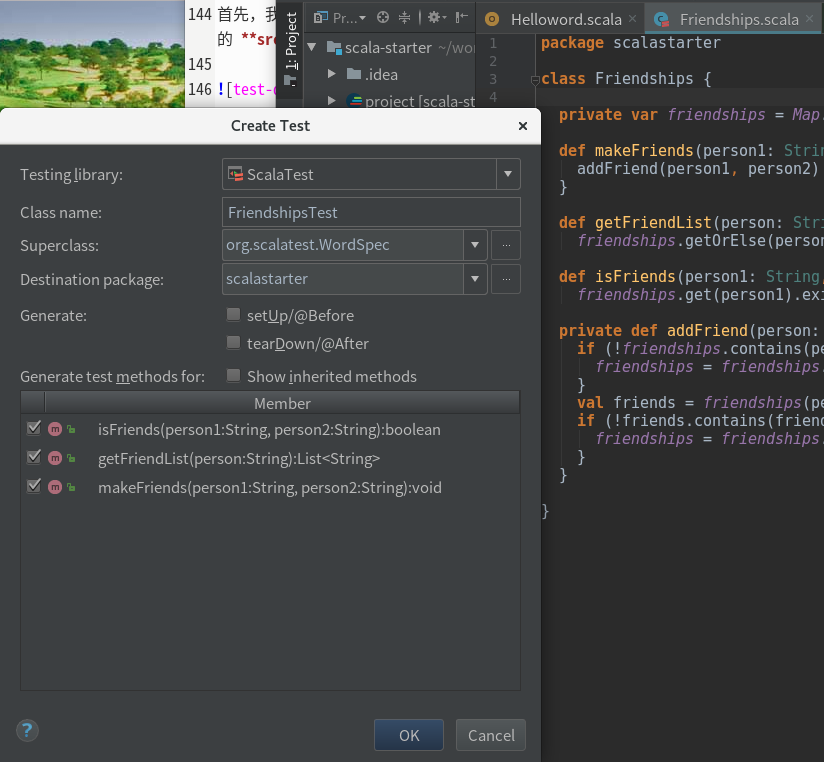
测试类 FriendshipsTest 代码如下:
1 | import org.scalatest.{BeforeAndAfterAll, MustMatchers, WordSpec} |
现在来运行下测试,两个测试方法 getFriendList 和 isFriends 都失败了。
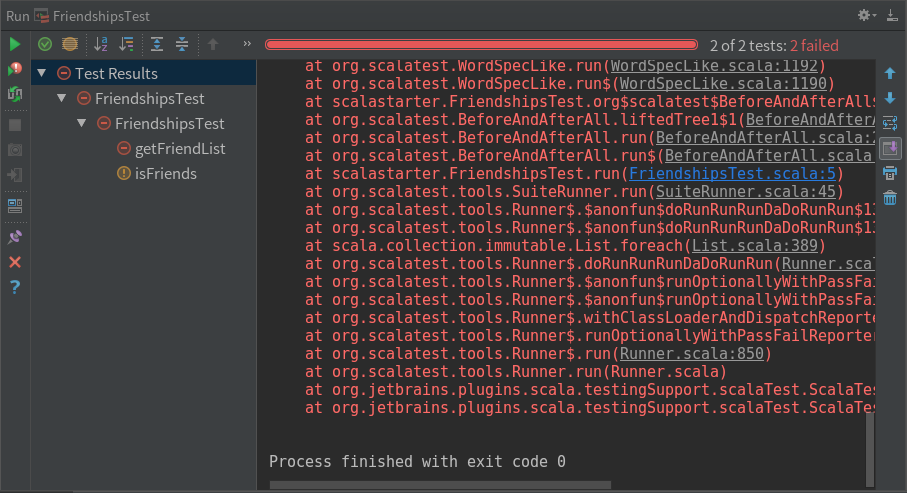
接下来让我们来完善 Friendships 类,把每个方法的实现都加上正确的逻辑。
1 | class Friendships { |
再次,运行 FriendshipsTest 测试,你将看到代表测试通过的绿色结果:All Tests Passed
总结
这一章从无到有,介绍了Scala工程项目的开发和TDD的实践上手方式。希望可以从工程方面带领读者踏入Scala的生态之旅。